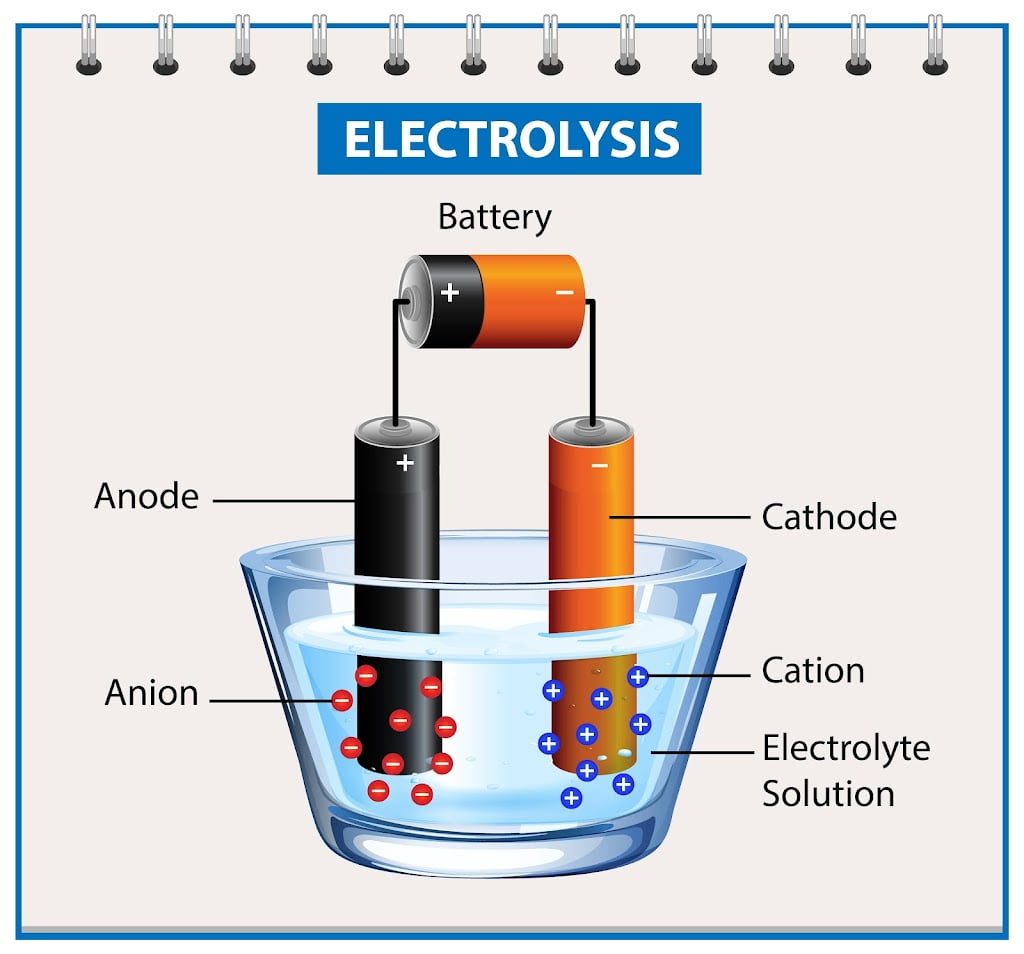
When it comes to batteries, the type of metal used can have a significant impact on its performance and longevity. In this article, we will explore the different types of metals that can be the best metals for batteries and can be used for batteries and their respective benefits and drawbacks.
Lithium-ion batteries (Best Metals for Batteries):
Lithium-ion batteries are currently the most commonly used type of battery for portable electronics such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets. The anode of these batteries is typically made of graphite, while the cathode is made of lithium cobalt oxide, lithium iron phosphate, or another lithium-based compound. These batteries offer high energy density, long cycle life, and low self-discharge rates. However, they are prone to overheating and can be dangerous if they are not used or handled properly, this property fetch it out in the list of Best Metals for Batteries.
Nickel-cadmium batteries:
Nickel-cadmium batteries, also known as NiCad batteries, were once the most popular type of rechargeable battery. They are made with a nickel hydroxide cathode and a cadmium anode. NiCad batteries are durable and can handle multiple charge and discharge cycles without significant degradation. They also have a low internal resistance, which makes them suitable for use in high-drain devices. However, they are environmentally unfriendly due to the toxic nature of cadmium, which can leach into the soil and water if not disposed of properly.
Nickel-metal hydride batteries:
Nickel-metal hydride batteries, also known as NiMH batteries, are similar to NiCad batteries in terms of construction but use a metal hydride instead of cadmium as the anode material. NiMH batteries offer a higher energy density than NiCad batteries, and they are also more environmentally friendly. However, they are not as durable as NiCad batteries and can suffer from memory effect if not charged and discharged properly.
Lead-acid batteries (Best Metals for Batteries):
Lead-acid batteries are the oldest type of rechargeable battery and are still used in a variety of applications today, including automobiles, boats, and backup power supplies. These batteries use lead plates and sulfuric acid electrolyte to generate power. Lead-acid batteries are relatively inexpensive, reliable, and can handle high discharge rates. However, they are heavy and bulky, have a low energy density, and are prone to sulfation if not maintained properly.
That why we consider it as a Best Metals for Batteries.
Zinc-carbon batteries:
Zinc-carbon batteries are the most common type of disposable battery and are commonly used in low-drain devices such as remote controls and flashlights. These batteries are made with a zinc anode and a carbon cathode. Zinc-carbon batteries are inexpensive and widely available, but they have a short shelf life and can leak if not used or stored properly.
Silver-oxide batteries:
Silver-oxide batteries are commonly used in watches and small electronics due to their high energy density and long shelf life. These batteries use a silver oxide cathode and a zinc anode. Silver-oxide batteries are more expensive than other types of batteries, but they offer a long lifespan and stable voltage output.
Alkaline batteries:
Alkaline batteries are the most commonly used type of disposable battery and are found in a wide variety of devices, including toys, flashlights, and digital cameras. These batteries are made with a zinc anode and a manganese dioxide cathode. Alkaline batteries are inexpensive and widely available, but they have a relatively short lifespan and can leak if not used or stored properly.
In conclusion, the type of metal used in a battery can have a significant impact on its performance and longevity. Each type of battery has its own set of benefits and drawbacks, and the best type of battery for a given application will depend on a variety of factors, including cost, energy density, and durability. Understanding the different




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.